Uncover Hidden Risks in Your Software Supply Chain.
Understand Your Risks Now.
Get started on the journey to understanding your total risk exposure.
Blind Spots in Your Software Supply Chain Can Cost You.
If you don’t know your risk your are vulnerable to undetected threats that can lead to costly data breaches, compliance violations, operational downtime, and long-term damage to your brand reputation. The RunSafe Risk Reduction Analysis gives you insight into your supply chain risk to take informed action to secure your embedded systems before it’s too late.
Analyze Your Exposure to CVEs and Memory-Based Zero Days
What to Expect
Prepare a binary and/or SBOM you want to analyze to determine your risk exposure.
Sign up for a Free Trial of the RunSafe Security Platform to start your analysis.
Upload your binary and/or SBOM to analyze your exposure, backed by novel academic research, to calculate the risk to your embedded systems.
Get a score of your total CVE and memory-based zero day exposure and risk reductions when runtime protections are applied.
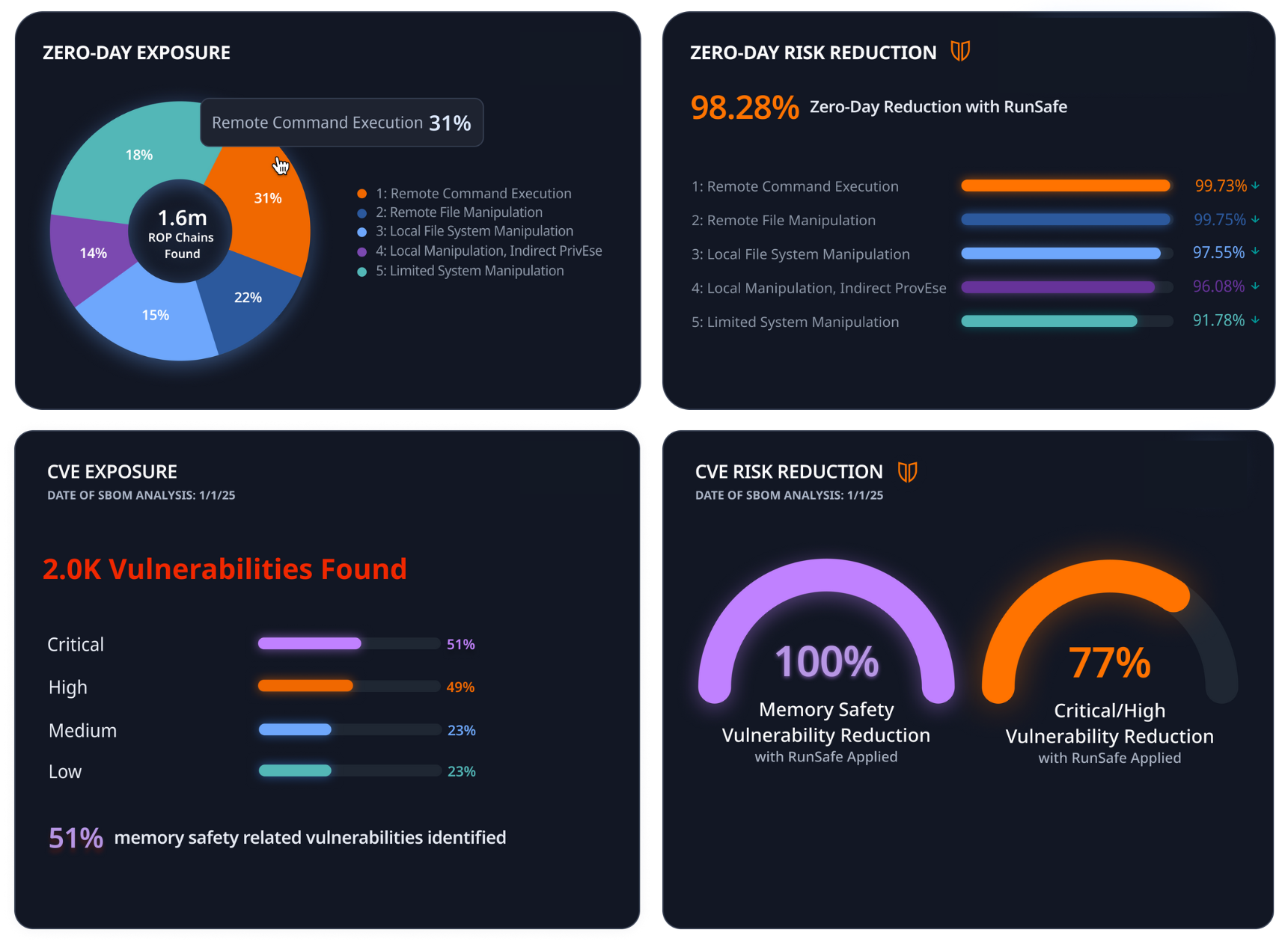
How It Works: Memory-Based Zero Day Exposure
Built on research from Linköping University, RunSafe’s Risk Reduction Analysis goes beyond scanning to analyze binary code for exploit-ready ROP (Return Oriented Programming) chains—a technique used in arbitrary code execution attacks for decades.
The analysis reveals exposure to memory-based zero days by quantifying the number of ROP chains that could be used by an attacker. It then shows how much risk shrinks after applying RunSafe’s patented memory relocation technology to minimize code misuse attacks.

Get a Risk Reduction Analysis Now
Get started on the journey to understanding your total risk exposure.